There are a handful of essential people kids learn about in school and during Black History Month: Martin Luther King Jr., Harriet Tubman, and George Washington Carver, just to name a few. But while these African American heroes in history have certainly made significant cultural contributions, there are many more that have fallen under the radar. To give your kids an ever-widening view of the world, learn about (and share!) these important Black history figures that have left a legacy for generations to come.
Alvin Ailey Jr.

Alvin Ailey Jr. was a dancer, choreographer, and activist. Born in Texas during the Great Depression, he moved to Los Angeles in 1946 and saw his first dance performance, and in 1949 he took his first dance class at Lester Horton's Melrose Ave. studio. When he formed the Alvin Ailey Dance Theater in 1958, he wanted to honor Black culture through dance. The company's first performance included Ailey's masterpiece, Blues Suite, and his most critically acclaimed work, Revelations, premiered in 1960. The company fused theater with modern, jazz, and ballet, and brought a multi-racial cast of dancers to the stage. Due to rampant racism at the time, few of these dancers would have found opportunities to perform with other companies.
In addition to choreographing pieces for his own company, Ailey created ballets for the American Ballet Theater, the Joffrey Ballet, and the Royal Danish Ballet, among others. He received numerous awards and honors over the years, including a Guggenheim Fellowship for Creative Arts in 1968, the Spingarn Medal from the NAACP in 1977, Kennedy Center Honors in 1989, and in 2014, he was posthumously awarded the Presidental Medal of Freedom.
John Lewis

John Lewis was born as the son of sharecroppers in rural Alabama in 1940. He studied at the American Baptist Theological Society in Nashville and helped to organize sit-ins against segregated restaurants; during this period, he coined his iconic phrase, "Good Trouble," and was jailed on numerous occasions. One of the original 13 Freedom Riders, his most memorable contribution to the Civil Rights Movement was "Bloody Sunday," when in 1965, he led a group of 600 over the Edmund Putts Bridge in Selma, AL. Beaten and left unconscious, Lewis caught the eye of Reverend Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., who joined them on another march from Selma to Montgomery, AL. John Lewis was elected to the United States House of Representatives for Georgia's 5th congressional district in 1987 and was re-elected to the office until he died in 2020. Among many honors and accolades, one of the most prestigious was the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2011.
Daisy Bates
When the Supreme Court ruled that segregated schools were unconstitutional, Daisy Bates stepped up to help a group of Black students integrate into an all-white high school—that group is known as The Little Rock Nine. In the face of constant fear and intimidation, Bates worked tirelessly to escort those young men and women to school every day and protect them from violent crowds. Daisy Bates was a lifelong civil rights activist, and her work is still recognized today. In the state of Arkansas, every third Monday in February is observed as Daisy Gatson Bates Day, and in 1999 she was Posthumously awarded the Medal Of Freedom.
Ruby Bridges
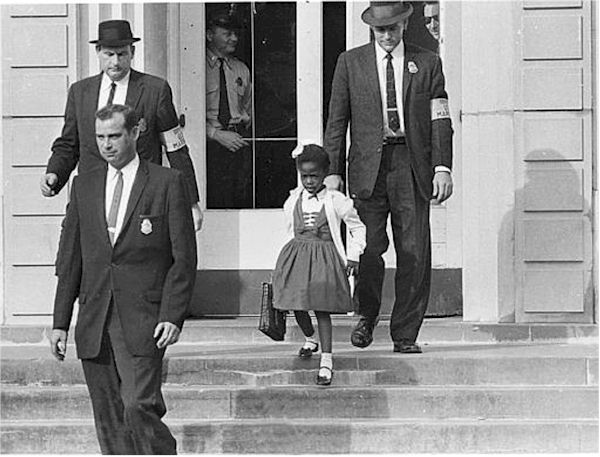

Ruby Bridges was the first Black student to integrate into a white elementary school in 1960. At only six years old, Ruby walked by protesters screaming awful slurs and angry words at her every day. And yet, she never missed a day of school. Ruby became a lifelong civil rights activist, and in 1999, she established the Ruby Bridges Foundation to help fight racism and promote tolerance and change through education.
Charles Drew
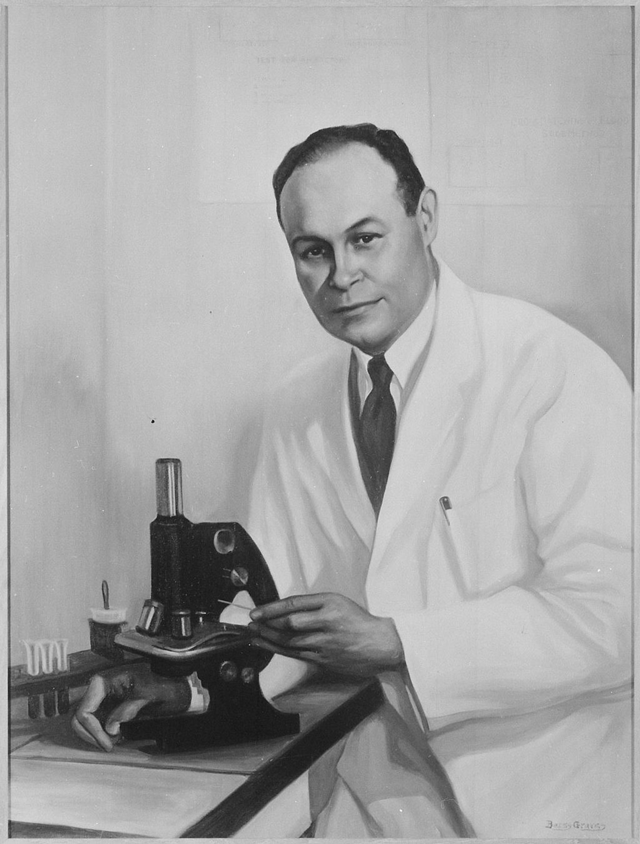

Charles Drew is considered a pioneer of blood plasma research and the modern blood bank. While in attendance at Columbia University, Charles Drew discovered the “shelf life” of blood could be extended by as much as seven days by separating and storing whole blood and plasma separately. Before that, blood could only be stored for up to two days. Charles Drew also wrote a dissertation Banked Blood: A Study in Blood Preservation, where he described the technique he developed and the logistics involved in the long-term preservation of blood plasma. Today Charles Drew is revered as the Father of Blood Banking.
Bessie Coleman
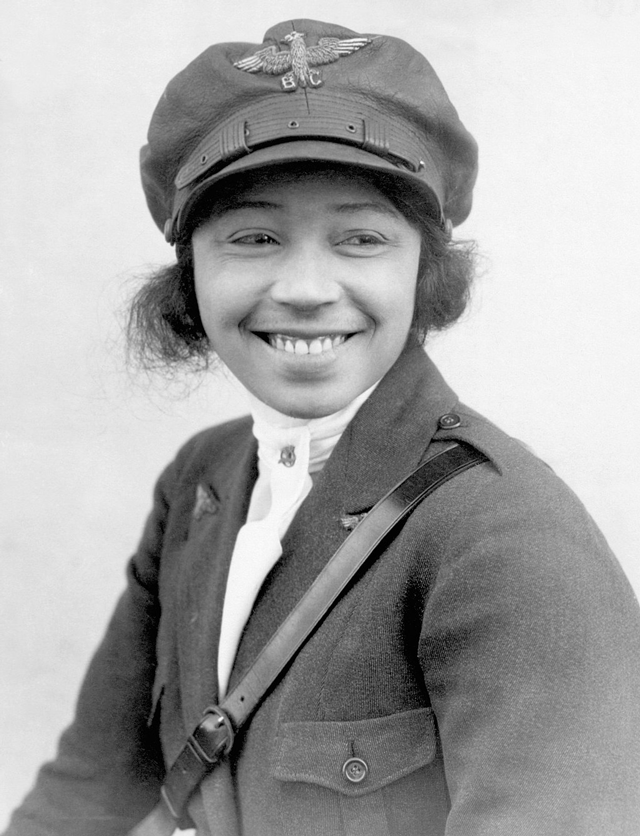

Look to the skies, and you'll be reminded about Bessie Coleman, the first Black and Native American woman pilot. Known for her amazing flying tricks, "Queen Bess" worked as a manicurist in Chicago when her brothers returned from World War I. When her brother John teased her that women in France were allowed to be pilots, Bessie took it as her mission to do just that. When no American flight school would take her, she learned French and moved to France to take flight lessons there.
When Bessie returned to the United States, she gave speeches and eventually performed her aviation tricks in air shows around the country. She famously refused to perform at any show where there was segregation or discrimination against African Americans. Bessie Coleman died in an air accident at age 34, and she was eulogized by the famous activist Ida B. Wells-Barnett.
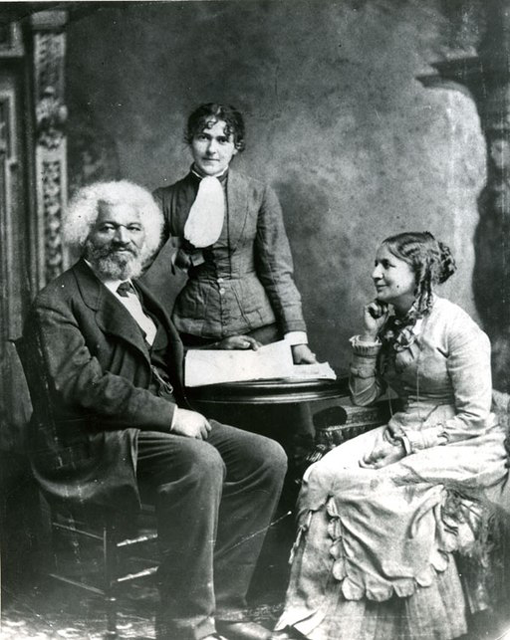
Frederick Douglass
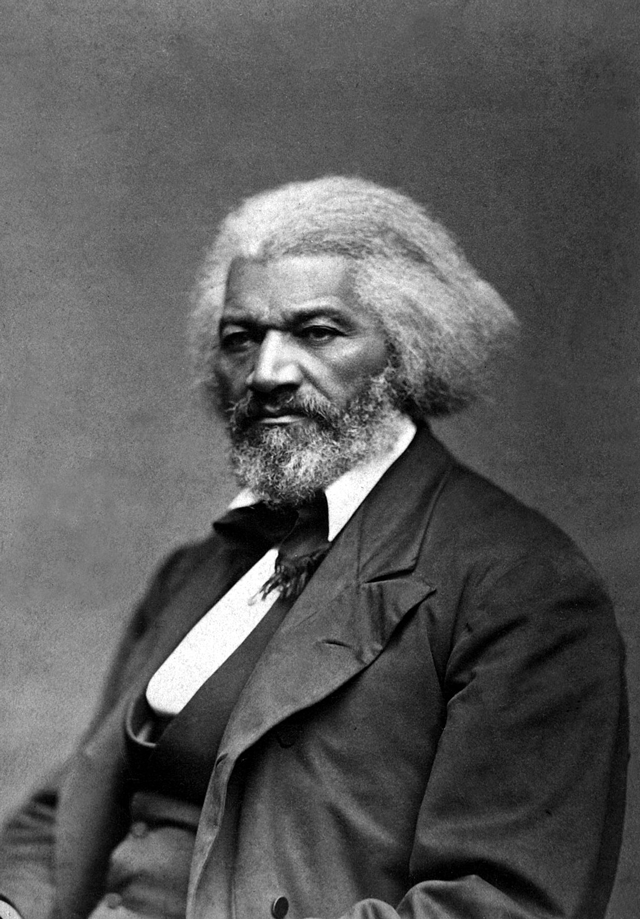

Frederick Douglass was a freed slave who spent his life outside of bondage as an author, an orator, and a leader of the abolitionist movement. Even after the Emancipation Proclamation in 1862, Douglass continued to champion equality, human rights, and even women’s rights. Douglass authored dozens of speeches and five autobiographies, the most notable of which is Douglass’ 1845 autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave. Here are 19 other interesting facts about Frederick Douglass.
Claudette Colvin

Claudette Colvin was an early activist in the civil rights movement in Alabama. Nine months before Rosa Parks refused to give up her bus seat to a white woman, Claudette Colvin did the same. At the young age of 15, Colvin was later arrested; violating the city’s segregation laws was among the many charges leveled against her. Colvin later told Newsweek, “I felt like Sojourner Truth was pushing down on one shoulder, and Harriet Tubman was pushing down on the other—saying, 'Sit down girl!' I was glued to my seat.”
Wilma Rudolph

As a young child, Wilma Rudolph battled a series of debilitating illnesses including double pneumonia, scarlet fever, and polio. She was forced to wear a leg brace, and doctors even told her she would never walk again. But Rudolph overcame her disabilities, and she was intent on pursuing her dreams. Her determination and natural athleticism eventually brought her to the 1960 Olympics, where she became the first woman to win three Gold Medals in Track and Field in a single Olympics.
Henry Ossian Flipper

A former slave, engineer, author, and American soldier, in 1877, Henry Ossian Flipper became the first African-American to graduate from West Point. Upon his completion, Flipper was also the first Black man to be commissioned in the Army (or any military branch, for that matter). After his commissioning, under the command of Captian Nicolas M. Nolan, he became the first Black man to lead buffalo soldiers of the 10th Calvery.
Rosa Parks

On December 1, 1955, Rosa Parks refused to give up her seat on the bus to a white woman. This act of defiance sparked the Montgomery Bus Boycott and created an impetus for change. One year after Parks' trial, the U.S. District Court for the Middle District of Alabama, Northern (Montgomery) Division, declared racial segregation laws (commonly known as "Jim Crow laws") unconstitutional. Considered to be one of the most important Black history figures, the United States Congress has called her "the first lady of civil rights" and "the mother of the freedom movement."
Daniel Hale Williams

In 1891, Daniel Hale Williams opened Provident Hospital in Chicago, IL. It was the first hospital with a racially integrated staff, a school for nurses, and also a training residency for doctors. In 1893, Williams was one of the first people to perform open-heart surgery, and he accomplished this feat outside of modern medicine and without the luxury of blood transfusions. He was also a co-founder of the National Medical Association, and in 1913 he was selected to be a charter member (and the only African American) of the College of Surgeons.
Alice Allison Dunnigan

Alice Allison Dunnigan was the first Black female White House Correspondent. She was also chief of the Associated Negro Press, and in 1948 she became the first Black woman to follow a Presidential campaign (Harry Truman’s) on the road. Years later, Alice Allison Dunnigan served as an education consultant on JFK’s Committee on Equal Employment Opportunity.
Robert Smalls

In 1862, during the Civil War, Robert Smalls commandeered a Confederate transport boat freeing himself, his crew, and their families. He sailed the ship to the Union-controlled region of Hilton Head, where it then became a warship. He was instrumental in convincing President Lincoln to let free Blacks serve in the Union Army. During the Reconstruction Era, Smalls was elected to the South Carolina House of Representatives and the United States House of Representatives, where he authored legislation that would allow South Carolina to have the first free public school system in the United States.
Jane Bolin

Jane Bolin was the first Black woman to graduate from Yale Law School, and in 1939, she became the first Black female judge. She was a huge advocate for children's rights: she served on the board of the Child's Welfare League, the National Urban League, and the NAACP, among others. Bolin also worked closely with then-First Lady Eleanor Roosevelt to establish the Wiltwyck School, a program to help eradicate juvenile crime among boys. Upon retirement, she volunteered as a reading instructor in New York public schools and served on the New York State Board of Regents.
Arturo Schomburg

Arturo Schomburg was a writer, historian, and activist. As a leader of the Harlem Renaissance, Schomberg collected art literature and other artifacts belonging to people of African descent. In 1926 his collection was purchased by the New York Public Library, and today the Schomburg Center is a research division of the NY Public Library. With more than 11 million items in the collection, the Schomburg Center is devoted to the preservation and exhibition of Black history and the arts and culture of the African diaspora.
Matthew Henson
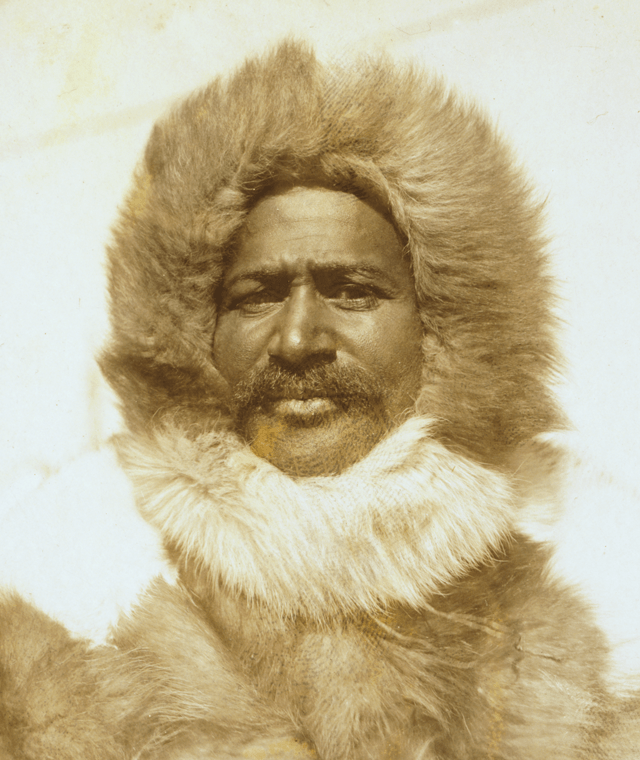

Matthew Henson is best known for his participation in a series of Arctic explorations between 1891 and 1909. But his claim to fame was the expedition that culminated in April 1909, where the team he was with finally reached the North Pole. Through these expeditions, Henson made significant contributions to the field of exploration. To honor those contributions, Matthew Henson was buried at Arlington National Cemetery with full military honors.
Shirley Chisholm
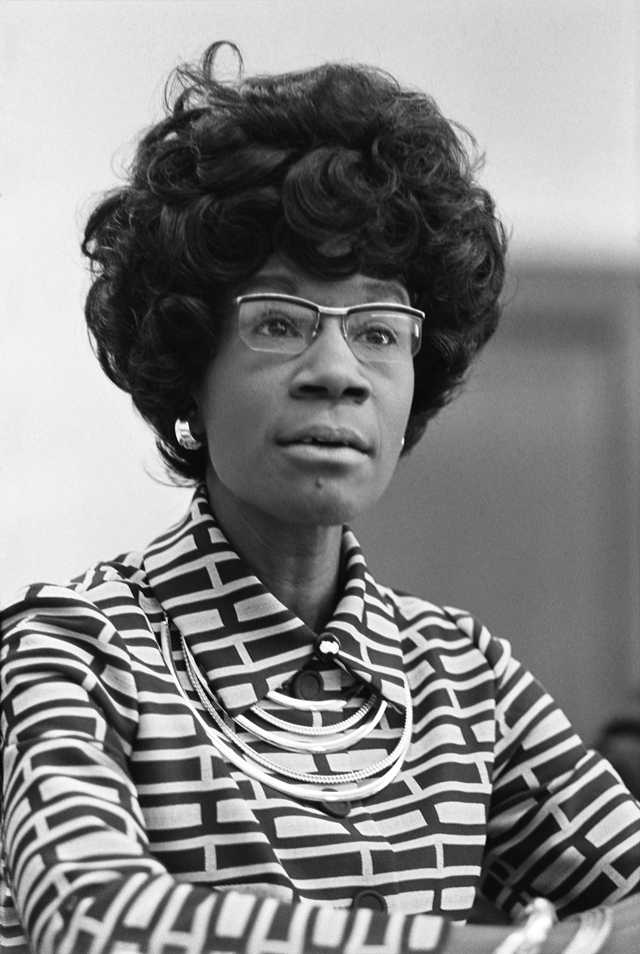

A true pioneer in both race and gender, Shirley Chisholm was the first Black woman elected to Congress representing NY’s 12th District. In 1972, she was also the first woman to run for the Democratic Party’s presidential nomination. During her time in Congress, Chisholm fought for improved education, health and human services, and women's rights. Chisholm famously said, “If they don’t give you a seat at the table, bring a folding chair.”
Fred Jones

In 1938, American inventor Fred Jones designed and patented a portable air-conditioning unit for trucks primarily used to transport perishable foods. Jones’ invention became invaluable during WWII when refrigeration units were used to preserve and transport food, blood, and medicine to hospitals and soldiers on the battlefield. In 1944, he became the first African American member of the American Society of Refrigeration Engineers. He was awarded 61 patents throughout his life, and in 1991, he was posthumously awarded the National Medal of Technology, the first African American to do so.
Dr. Rebeccca Lee Crumpler

Dr. Rebecca Lee Crumpler was the first female African-American physician. She also wrote the Book of Medical Discourses in Two Parts in 1883, which is considered one of the first medical texts written by an African American author. After the Civil War, Dr. Crumpler also worked for the Freedman’s Bureau for the State of Virginia, the federal agency that helped over 4,000,000 slaves make the transition from slavery to freedom.
Gwendolyn Brooks
Gwendolyn Brooks was an American teacher, poet, and author. During her life, Brooks authored over 20 books of poetry and one novel. In 1950, Gwendolyn Brooks was the first African American to win the Pulitzer Prize. Among countless other honors and awards, in 1968, she was named poet laureate for the state of Illinois, in 1976, she became the first African American woman to be inducted into the American Academy of Arts and Letters, she was the U.S. Poet Laureate for the 1985-86 term, she was inducted into the National Women's Hall of Fame in 1988, and in 1995, she was awarded the National Medal of Arts.
Katherine Johnson
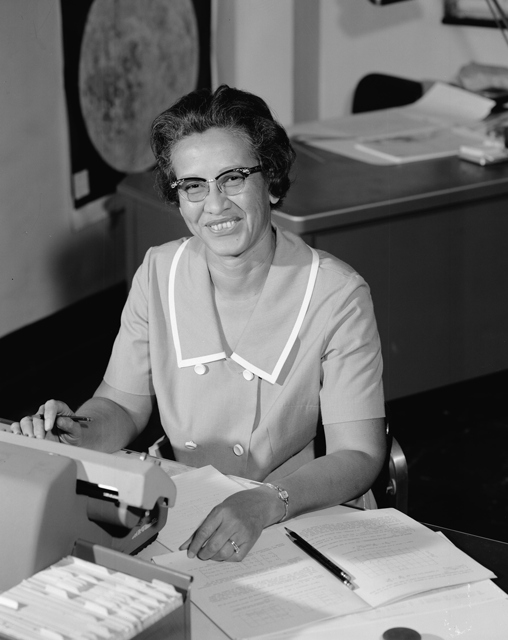

In 1962, Katherine Johnson's brilliant math skills were called upon to help put John Glenn into orbit around the Earth. John Glenn requested that Katherine herself double-check the orbital trajectory of the Friendship 7 from liftoff to splashdown; only then would he carry on with the mission. Later in her career, Johnson also worked on the Apollo Moon Landing project as well as early plans for a mission to Mars. Katherine Johnson also co-authored 26 scientific papers, which can still be found in the NASA archives.
Mae C. Jemison

Mae C. Jemison is an American physician and astronaut. In 1987, Jamison was the first African American woman to be accepted into NASA’s astronaut training program. In 1992, Jemison was also the first African American woman in space, flying there aboard the spaceship Endeavor with six other astronauts.
Maya Angelou
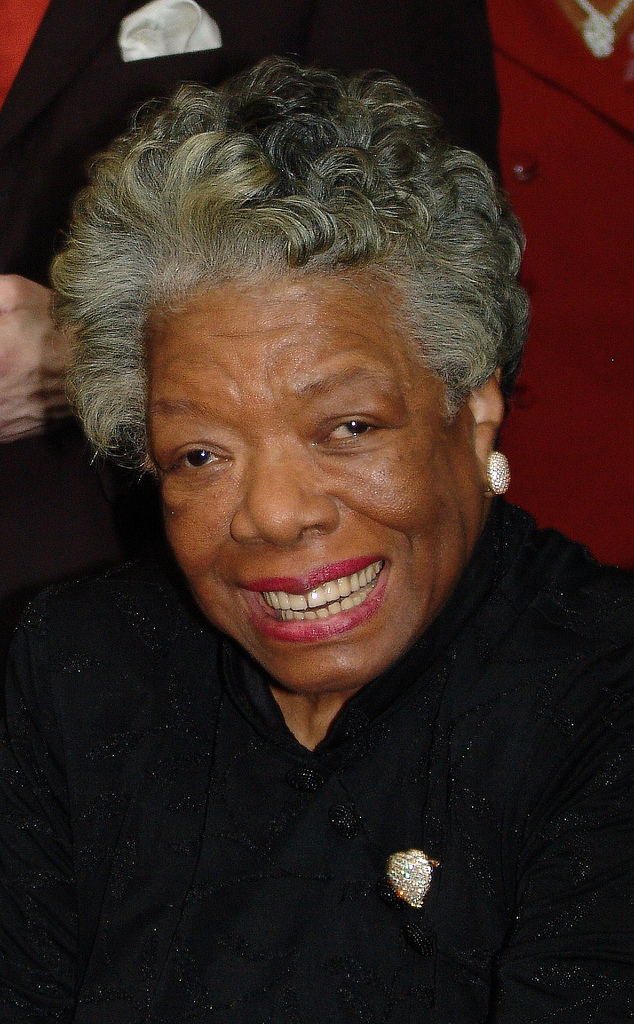

With more than 30 bestselling titles, Maya Angelou wrote 36 books, not the least of which was her first book I Know Why The Caged Bird Sings. Although she died in 2014, Maya Angelou is remembered as a brilliant writer, poet, and civil rights activist. Oprah Winfrey said of her friend, “Maya Angelou is not what she has done or written or spoken, it’s how she did it all. She moved through the world with unshakeable calm, confidence, and a fiery, fierce grace and abounding love.”
Ron Finley
As a young man growing up in South Central LA, Ron Finley was all too familiar with the lack of fresh produce. Determined to change that, Finley started a garden on a dirt patch on the sidewalk outside of his home. When the city cited Finley for gardening without a permit, he rallied other “green activists” and petitioned for the right to grow food in his neighborhood. Finley won, and today he is affectionately known as “The Gangsta Gardener.” Now a community leader, Finley is determined to help urban communities break out of their "food prisons." Finley has traveled extensively speaking publicly on the topic, and he has even done a TEDTalk that has been watched by over three million people.
Alice Coachman

Alice Coachman was the first Black woman to win an Olympic Gold medal from any country. Born on November 9, 1923, in Albany, Georgia, she was the fifth of 10 children born to Fred and Evelyn Coachman.
At the time, it was considered "unladylike" for women to be interested in sports. Her parents agreed with this thinking and often punished Coachman for participating in activities like running and baseball. While she never considered a career in sports, by the 7th grade, she was one of the best athletes in Albany, boy or girl. Since the South was still segregated at this time, Coachman often ran shoeless and created her jumping equipment, as she was unable to use public facilities reserved for white kids.
She transferred to the Tuskegee Institute during her sophomore year of high school, and as a member of their track-and-field team, Coachman won four national championships in the high jump and sprinting categories. As one of the best track-and-field athletes in the country, she continuously won titles in the 50m, the 100m, and the 400m relay, although her favorite was the high jump.
She tried out for the 1948 US Olympic team and broke the World Record for the high jump during the trials. In August of 1948, she became the first Black woman and the first American woman to win an Olympic gold medal.
Even though her Olympic career ended with an injury at 24, Coachman went on to finish college and become an elementary and high school teacher and a track coach. She was inducted into multiple Hall of Fames for her abilities and founded the Alice Coachman Track and Field Foundation to help athletes and former competitors in financial need. Coachman died in 2014 at the age of 90.